Made in Korea
FDA Approved
Cost Effective
100% Safe
Customizable
FDA Approved
Korean Suture in the Philippines
OAK TREE® Sutures aims to provide SURGEON’S CHOICE for SAFE and SECURE wound closure. Our mission is to provide TAILORED PRODUCTS to meet the specific needs of the wound closure segment and help healthcare professionals and hospitals nationwide.

Surgeon’s choice for Safe & Secure wound closure
Products
Our world class product passed several national and international regulatory audits such as CE, ISO, FDA, and various international registration
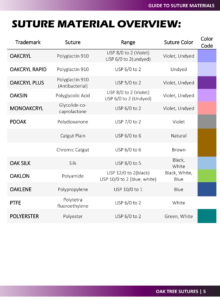
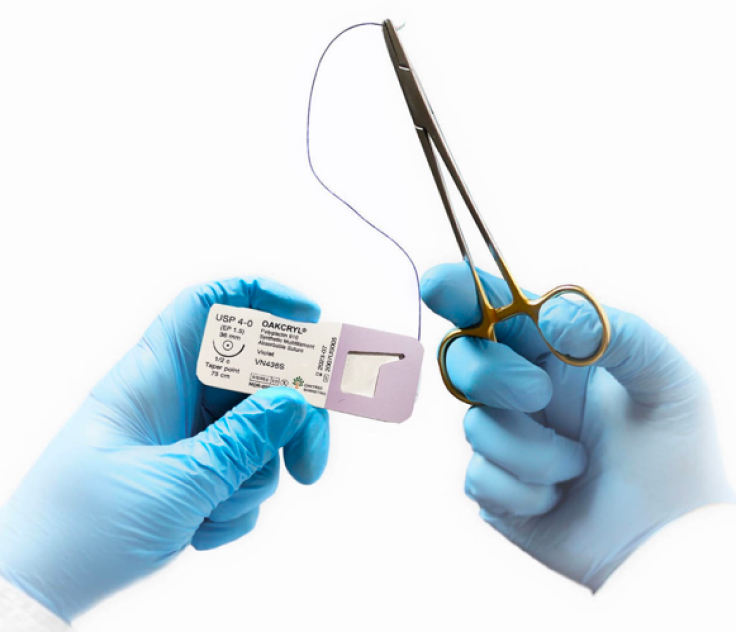
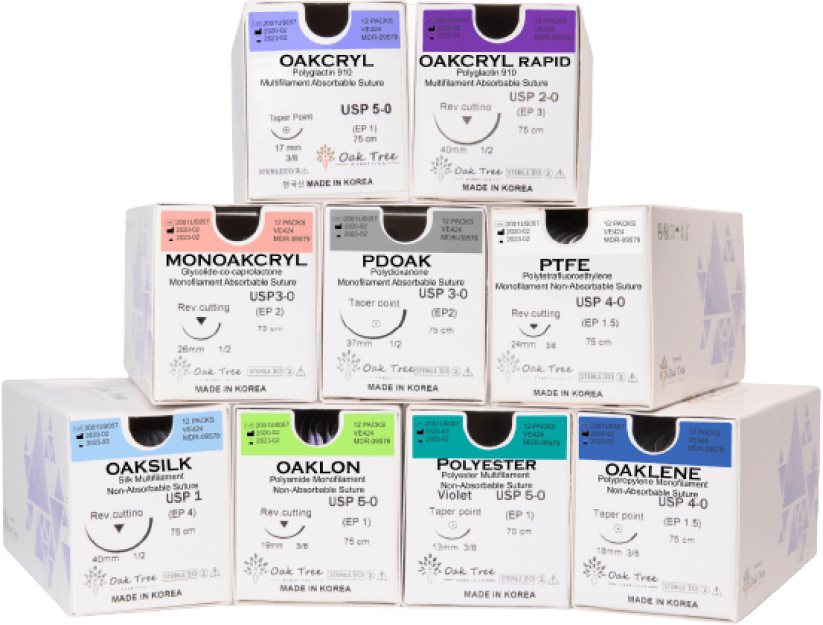
OAKCRYL Polyglactin 910 Suture
OAKCRYL® Suture is a synthetic absorbable, braided, coated suture composed of a co-polymer made from 90% glycoside and 10% L-lactide and is both available in dyed and undyed form.
Monofilament Nylon Sutures
Nylon Polyamide Non-absorbable suture, composed of Polyamide 6 and Polyamide 6.6, guarantees extended, enduring tensile strength in tissue. Crafted from a single strand, it facilitates smooth passage through tissues, reducing trauma and the risk of infection by minimizing bacterial growth. Its flexibility enhances ease of use for skin sutures, and the inherent properties of nylon enable the production of exceptionally fine threads, making it a popular choice for ophthalmic surgery and microsurgery.
OAKSIN
Polyglycolic Acid
Multifilament
Violet or Undyed
Tensile Strength: 50%- 21days
Complete Absorption: 60-90 days
MONOAKCRYL
Glycolide-co-caprolactone
Monofilament
Violet or Undyed
Tensile Strength: 50%-10 days
Complete Absorption:
90-110 days

OAKSILK
Silk
Multifilament Braided fibers
Black or White
OAKLON
Polyamide Nylon
Monofilament
Black, White or Blue

OAKLENE
Polypropylene
Monofilament
Blue

OAKPTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene
Monofilament
White

OAKSTER
Polyester
Multifilament Braided
Green or White
Clients





































Our Certificates

Philippine Dental Association

Philippine Academy of General Dentistry Inc.

Philippine College of Oral Implantologists

LUCON Philippine Dental Association

Asia Pacific Academy of Implant Dentistry
FAQs
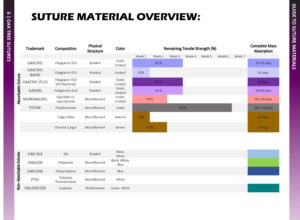
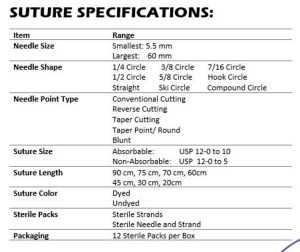
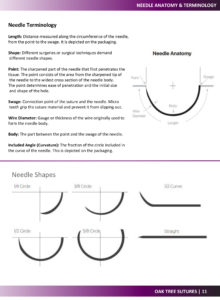
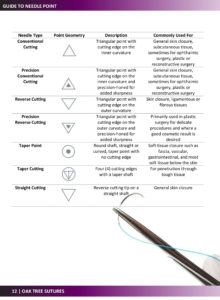
Guide to Suture Materials
What is the difference between Absorbable VS Non-Absorbable Suture?
Sutures that lose the majority of its tensile strength within 60 days are considered absorbable. It is degraded by tissue enzymes or hydrolysis.
- Absorbable sutures are generally used as deep sutures; it does not need to be removed post-operatively.
- Non-absorbable sutures are used for surface sutures; require manual removal post-operatively.
What is the difference between Multifilament VS Monofilament Suture?
- Multifilament braided sutures handle more easily and tie well, but can potentially harbor organisms between fibers leading to increased infection risk. They should be avoided in contaminated wounds. They also tend to have higher capillarity so can absorb and transfer fluid more easily increasing potential for bacteria to enter from the skin surface.
- Monofilament sutures have a lower infection risk and a lower coefficient of friction, but with a lower ease of handling and knot security.
What is the difference between Synthetic VS Natural Suture?
- Synthetic sutures Synthetic sutures consist of human-made materials, such as nylon. It tends to be less reactive than natural materials. It tend to lose tensile strength and be absorbed at more predictable rates.
- Natural sutures Natural sutures originate from a biological source. Silk is an example of a natural suture material. It is derived from purified animal tissues (usually collagen) and are sometimes made of the purified serosa of bovine intestines.
Events

UECD DENTAL TRADE FAIR
DENTAL TRADE FAIR 5th Floor, UE Manila Annex | July 17 - 18, 2025

PDA – Bulacan Chapter 5th Scientific Seminar & General Assembly Dr. Jose Angelo G. Militante
UNUSUAL COMPLICATIONS IN ORAL SURGERY Hiyas Convention Center, Malolos City, Bulacan | March 5, 2025

PCOI MIDYEAR SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR
Synergy in Implant Dentistry: Shutter and Surgery National University, MOA, Pasay City | June 5, 2025
Contact Us
Fill up the form below.